- Finance and people’s access to financial instruments occupies a great space in the debt economy of capitalism.
- Goldfinch protocol, one of the decentralized finance applications, facilitates access to financial instruments by connecting the real-world economy with the crypto economy.
- Goldfinch utilizes their own trust through a consensus mechanism instead of the over-collateralization method, which we typically see in DeFi applications.
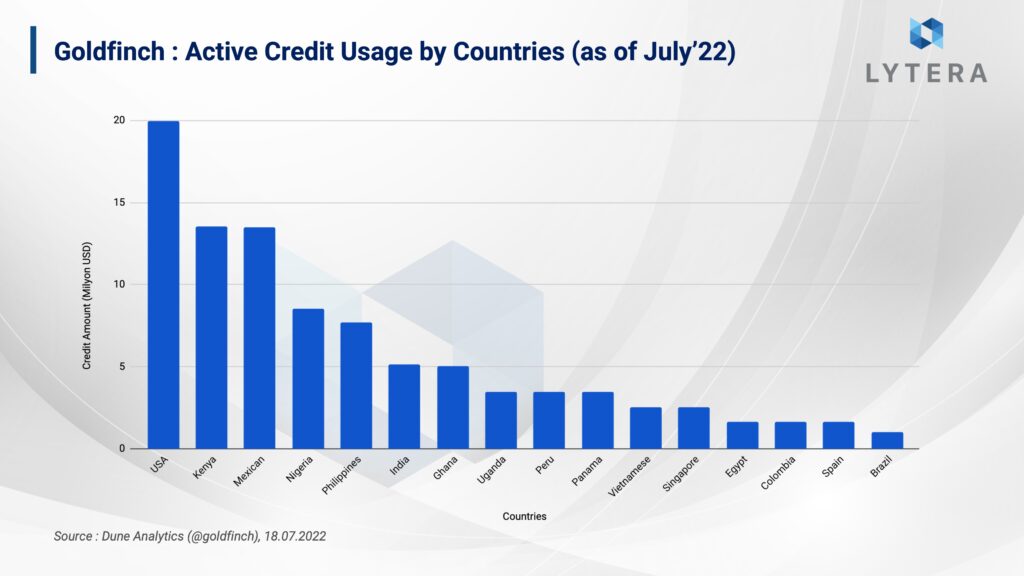
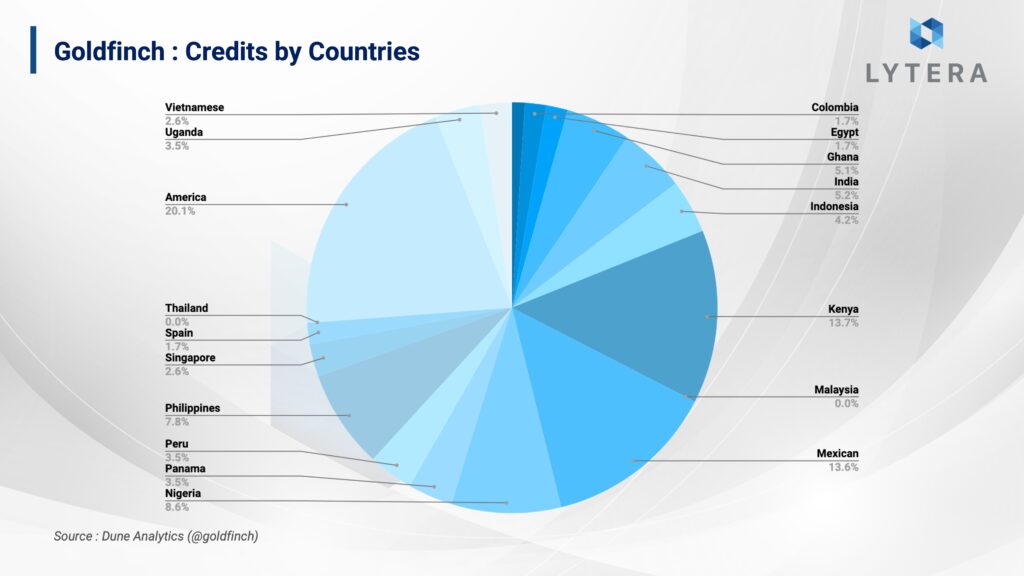
- Goldfinch has provided $100 million in loans to businesses so far. Among the countries where the businesses receiving these loans are located are the United States, Kenya, Nigeria, the Philippines, and Mexico.
- Goldfinch ecosystem consists of Backers, Auditors, Liquidity Providers, and Borrowers; and all these actors have to act in harmony with one another in order to ensure the smooth operation of the system.
Microfinance and Macroeconomics
Finance plays an important role in the growth and development of developing countries within capitalism. Considering the issue on a country basis, states utilize various instruments of finance in order to create funds, reduce borrowing, and accelerate hot money flow. Moreover, they occasionally launch microcredit programs to accelerate production activities and to support projects and persons who would create added value for the domestic economy of the country. These microcredit programs may range from agriculture to technology, from logistics to small businesses. According to an ongoing study since 2012, mainly examining the microcredit programs of developing countries, microcredit programs are of great importance in terms of increasing the gross national product of the country, enhancing the welfare level of citizens and generating projects that would add value to the country’s economy. While microfinance has importance on countries, it should be noted that it affects individual citizens as well.
Developed countries have greater opportunities in terms of accessing financial instruments and loans compared to developing and underdeveloped countries. A great number of adults in the world population do not have the opportunity to have a bank account or access to financial instruments, and the majority of this segment consists of the people living in African and South American countries. According to a survey conducted in 2021, it is seen that the top 5 countries in terms of bankless citizens are Morrocco with 71%, Vietnam with 69%, Egypt with 67%, the Philippines with 66%, and Mexico with 63%. Moreover, even if the individuals are able to access banking services, it is not possible for them to access a great number of financial instruments, mainly credit products, due to collateral problems. Decentralized finance can provide most services that traditional finance fails to provide and grant individuals the opportunity to be their own banks. Among many lending platforms in the crypto ecosystem, Goldfinch project shows a relatively more centralized but an indirect solution-oriented approach.
Goldfinch Nedir?
In the simplest terms, Goldfinch is a credit platform running on Ethereum, providing liquidity to finance and technology companies. One of the main objectives of the platform can be defined as increasing the number of users in the lending-borrowing system and making a difference in the overcollateralization system in decentralized finance. One of the reasons why DeFi is not able to have a broad effect on the end users is the overcollateralization system. Goldfinch aims to solve this problem through their own “trust through consensus” method. One of the distinguishing aspects of Goldfinch compared to other credit platforms in the ecosystem is that the credits given appeals not only to the individuals and organizations within the crypto ecosystem but also businesses operating in the real economy. In this way, the protocol builds a bridge between real economy and crypto economy. Currently, there are organizations in 28 different countries utilizing Goldfinch to develop businesses in their own regions and to give microcredits to people living in the region. Anyone can participate in the credits given in the protocol and earn passive yield from the interest received. In the following sections of this article, detailed information will be given about the actors of the system and how it works.
Normally, if someone wants to borrow on-chain using lending platforms such as AAVE and Compound, they need to deposit more collateral than they want to borrow. The reason for this is the lack of credit certification agency working with a central government on chain unlike banks. Since the actor who wants to borrow typically do not have the collateral, the lending mechanism on DeFi protocols only benefits the leveraged positions and arbitrageurs instead of the end user. In order to solve this problem, Goldfinch created a new system that can be called a credit approval committee within the trust through consensus mechanism. The actors of this system are Borrowers, Backers, Liquidity Providers, and Auditors.
- Borrowers consist of FinTech enterprises which are operating in traditional finance. Due to cumbersome bureaucracy for borrowing or investment collection as well as high interest rates in especially developing countries, borrowing through DeFi becomes more attractive. Hence, these businesses prefer Goldfinch as a novel option.
- Backers are the key team in the protocol. Backers can also be considered as angel investors. After businesses desiring to get loans submit their application to the protocol, the financiers (backers) are the first ones to review it. In case the backers deem the application for the loan is suitable, they provide the initial capital themselves.
- Liquidity Providers can consist of anyone who provides liquidity to the main USDC pool, i.e. Senior Pool, not dedicated to any specific business/loan, After the Backers’ approval of the loan application and provision of initial capital, the amount in Senior Pool are distributed pro rata to the first-loss capital by the financier to the Borrower Pools opened by the businesses. To add liquidity to Senior Pool, KYC (Know-Your-Customer) verification via Persona or Parallel Markets is required.
- Auditors are the ones approving whether the business will receive the loan or not. In order to become an Auditor in the protocol, it is necessary to stake a certain amount of GFI. This helps the protocol prevent possible sybil attacks and increase the quality of Auditors.
How Trust Through Consensus Mechanism Works
First of all, businesses that want to get a loan have to open a Borrower Pool on the platform. This pool consists of Junior Tranche and Senior Tranche. When opening this pool, the businesses have to specify the interest they are willing to pay, the frequency of their repayments, the maximum amount that can be withdrawn from the pool, and the default interest. Additionally, the businesses must also add their field of business, how they will utilize the borrowed amount, and information on their team members. Borrower Pool is actually similar to an engagement letter submitted to Goldfinch. After this process, the auditors decide whether the business is eligible for a loan after evaluating the pool and the terms. In case the business is eligible for a loan, then the backers step in.
Backers are free to choose the businesses they wish to invest in among the applications received by the protocol. After the engagement letter is submitted during the application, the backers and businesses applying for a loan may decide to come together to negotiate and improve terms, and decide whether they may invest or not by assessing the off-chain records and financial history of the business. In case the business convinces the backers, they add the first-loss capital to the junior tranche within the borrower pool. The reason why it is called “first-loss capital” is that the loans to be withdrawn by the businesses from the pool will be initially covered from this part; and in case of a failure to repay, the capital which would be subject to loss will be undertaken by the backers.
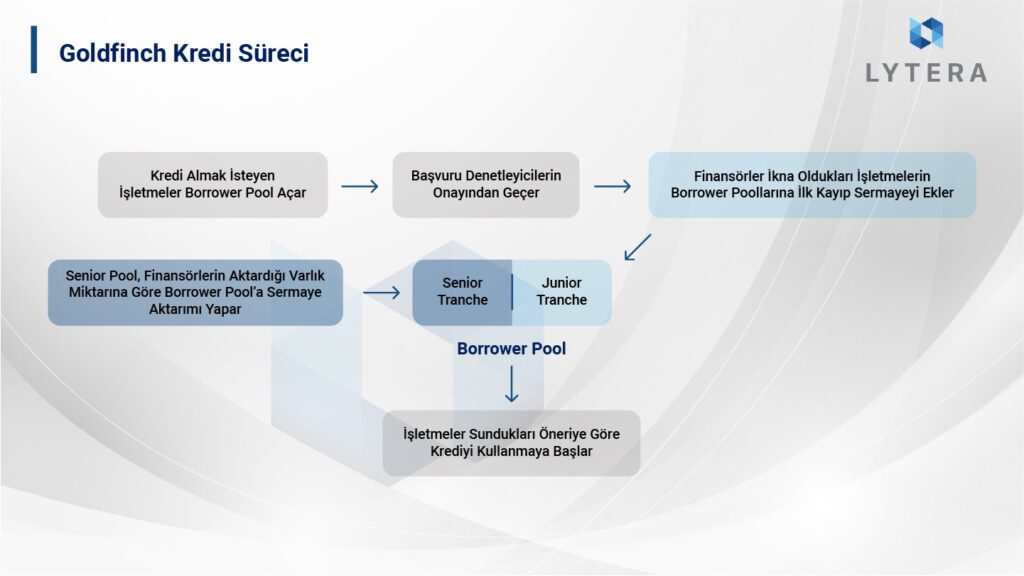
After adding first-loss capital, staked USDC in the Senior Pool, where liquidity providers stake their capital, are added pro rata to the capital transferred by the backers on the condition that the smart contract regards the Borrow Pool safe. Following this process, borrower enterprises receive the loan and start processing in accordance with the terms specified in the beginning, and are expected to repay in accordance with the agreement at the time of interest repayment.
Another point that we should address here is the return that backers, liquidity providers, and the platform receive from lending. As backers take a higher risk, their return rate is higher compared to the other actors. The most important reason for this is that they are the ones providing the first-loss capital. To exemplify: Let us assume Business A applied for a $5 million loan through Goldfinch, approved by the auditors, and the backers deposited $1 million as the first-loss capital, and the remaining part of the loan was borrowed from Senior Pool, where liquidity providers deposit their assets. When Business A repays the loan with the interest within the given period, the amount of interest repaid is distributed to all actors in the following manner:
Bir örnek vermek gerekirse, A işletmesi Goldfinch protokolü üzerinden 5 milyon dolarlık bir kredi için başvurdu, denetçiler tarafından uygun görüldü ve finansörler ilk kayıp sermaye olarak 1 milyon dolar sermaye yatırdılar, kalan 4 milyon dolar da likidite sağlayıcılarının dahil olduğu Senior Pool’dan geldi. A işletmesinin alınan krediyi verilen süre içerisinde faiziyle ödediği durumda geri ödenen faiz tutarı şu şekilde tüm bileşenlere dağılıyor;
- Senior Tranche Return (Liquidity Providers): gross interest (%12 in this case) – protocol reserve share (10%) – reallocation fee (20%) = net interest return (8.4%).
- Backer Return (Backers) : gross interest (12%) – protocol reserve share (10%) + reallocation fee (20%) = net interest return (20.4%)
As backers take on a greater risk, the interest return they will receive is higher than liquidity providers compared to liquidity providers whose net returns are less risky.
Goldfinch in Figures
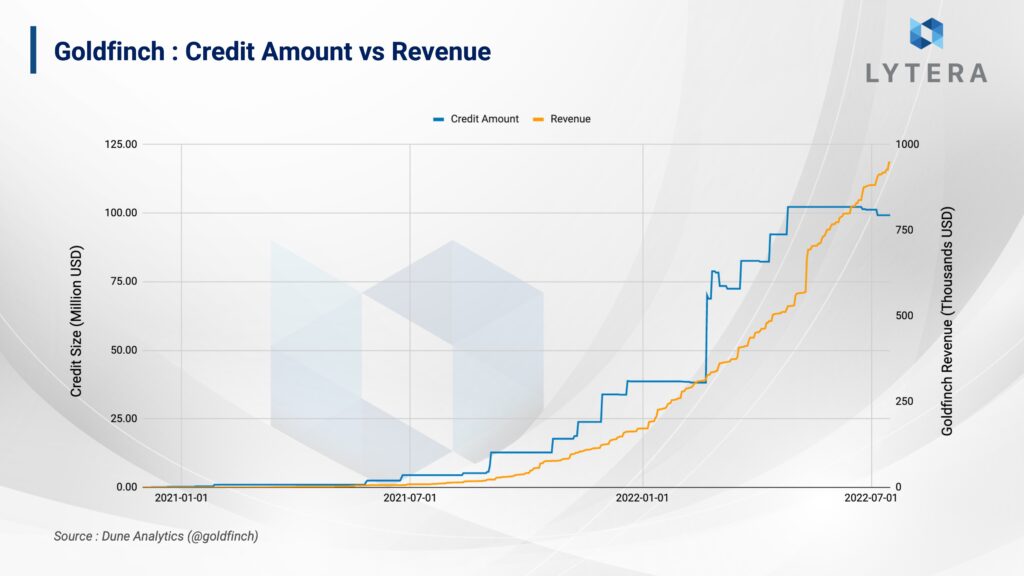
So far, Goldfinch has provided loans of approximately $100 million to many businesses such as Stratos, Almavest and Cauris. While some of these businesses provide customized microcredits for the people in their region, others make institutional investments. For instance, while Stratosis a company that both provides consultancy services and acts as an investor in fintech companies in the United States, Quickcheck provides consumer loans to its middle and lower class customers in Nigeria, and Payjoy provides loans to its customers for smartphone purchases in Mexico.
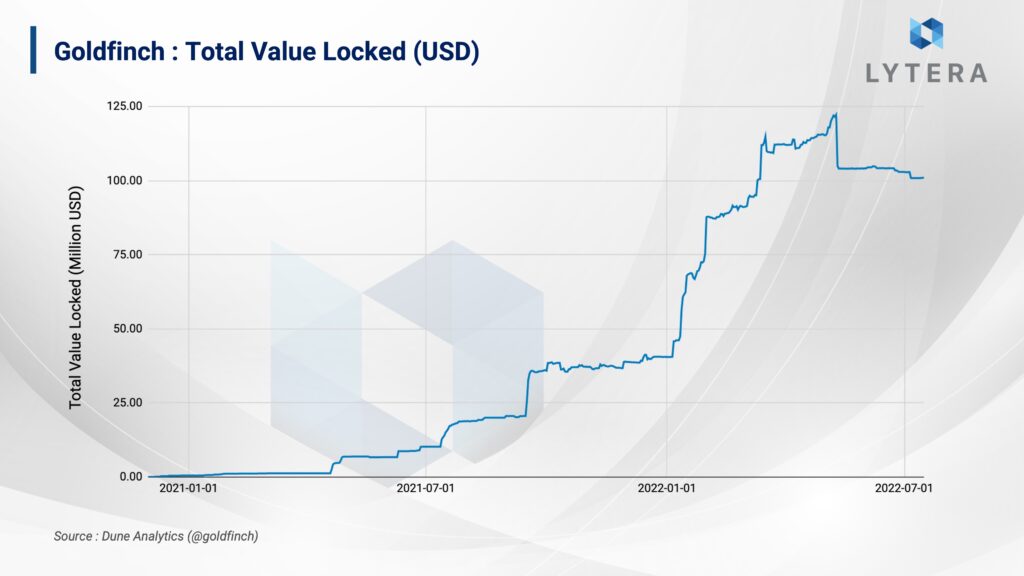
Businesses borrowing from the platform mainly consist of intermediary loan platforms established to increase financial and technological activities and to include people in the financial sector in developing countries. Cauris Fund, which opened a Borrower Pool for the third time, provides loans to businesses that would open the door to finance for the unbanked population in the African continent.
The revenue collected since the beginning of 2021 is approximately $5.1 million. Of this amount, $4.2 million has been distributed to the liquidity providers and the financiers while $881 thousand is registered as revenue to the protocol itself.
To date, Golfinch has provided a total of over $100 million in loans to businesses. Above, we have mentioned that the participation in the protocol is mostly from developing countries. The loans received through Goldfinch seem to be mostly from companies located in Kenya, Mexico, Ghana, Nigeria and the United States.
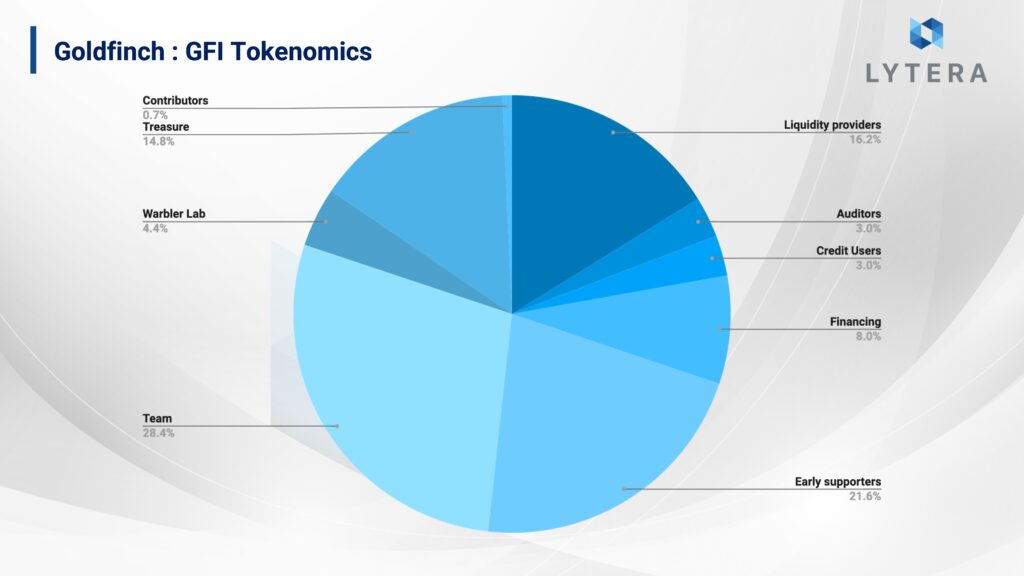
GFI and FIDU
Total supply of Goldfinch’s governance token is 114,285,741 and is planned to be distributed to many actors in certain proportions. The majority of these shares are allocated as team, early investors and liquidity mining rewards. 4% of total tokens allocated as liquidity mining rewards (16%) was distributed to people who provided USDC liquidity to Senior Pool until December 14, while 4.2% of it was allocated to people who provided USDC until July 2021 with a 6 month linear vesting, and the remaining 8% was reserved for Senior Pool liquidity providers, which is still in progress. In order to incentivize the backers, 8% of GFI tokens are allocated. 2% of this allocation is reserved as a certain amount of GFI as rewards for every 1 USDC paid, 2% as GFI rewards who complete the tasks within the scope of Flight Academy, and rewards to be paid upon staking GFI on other backers, which will be put into practice in the future.
There is another token with the ticker FIDU that holds liquidity information deposited to the platform. There are two different liquidity mining yields on Senior Pool. The first is obtained directly as USDC, the other is the distribution of GFI. After adding liquidity to the pool, the platform mints FIDU tokens in return. For GFI liquidity mining, FIDU tokens received have to be added to FIDU-USDC pool on Curve. Afterward, it is possible to earn both USDC and GFI tokens from the liquidity added to Senior Pool.
Conclusion
Goldfinch is a rather different position compared to many projects in the current crypto ecosystem due to its real-life adaptability. Probably the area where the crypto ecosystem is credit platforms, which can have the highest effect with the ability to provide a bridge between two worlds. Hence, it both facilitates the adaptation process of crypto and enhances the area of impact while establishing a connection between the bankless and finance. Although currently, Goldfinch’s lending process only covers corporate businesses, there is a mechanism that opens the door to on-chain individual loans in the following years. Moreover, in line with the last two years as we have seen institutional adoption of crypto with a stronger interest, it can be argued that on-chain record keeping by businesses on blockchains may be a factor which can increase or decrease people’s trust in these businesses.
In their statements, Goldfinch team claims that the protocol does not correlate with the overall crypto ecosystem and that volatility of crypto markets does not have a dramatic effect on the project. This discourse may be considered valid for certain situations because liquidity providers or borrowers of the platform use USDC, and the amount of interest to be earned/paid is also calculated over US dollars. As it does not use the overcollateralization method like other protocols, the platform is not affected by any fluctuations in crypto markets. On the other hand, when the crypto markets turn bearish, investors usually return to stablecoins, which seem safer in the ecosystem, and they stake their stables to certain protocols to have some passive income. Since Goldfinch’s credit mechanism is built on interest rates determined over real world, annual interest rates are usually higher than other DeFi protocols, which may help them to turn the negative trend into positive for the protocol. Even though Goldfinch distinguishes itself from the general crypto markets, macroeconomic crises may make the platform just as risky. Furthermore, while lenders utilize stables and engage in the system considering sustainable business models and possible macro crises, it should be noted that the real economy may face unexpected situations such as the COVID pandemic. One of the sectors which may be affected the most in such crises is the financial sector. In such a case, the delay or inability of businesses to repay their loans may put the protocol in a major crisis.
Goldfinch is planning to open secondary markets in the future in order not to experience a liquidity crisis, to keep capital flowing into the platform and to increase the number of backers. These secondary markets are envisioned to enable backers who have already deposited capital to a Borrower Pool to sell their positions in that pool to another backer. Since the repayment plans cover long time periods, these secondary markets will enable backers who already have a position to acquire capital to join the new Borrower Pools in addition to providing an opportunity to new backers who wish to have a position in a pool but not able to join the pool because the deposit period is closed. When these secondary markets become a reality, the cash flow and the increase in deposits may have a great importance both for borrowers and investors.




